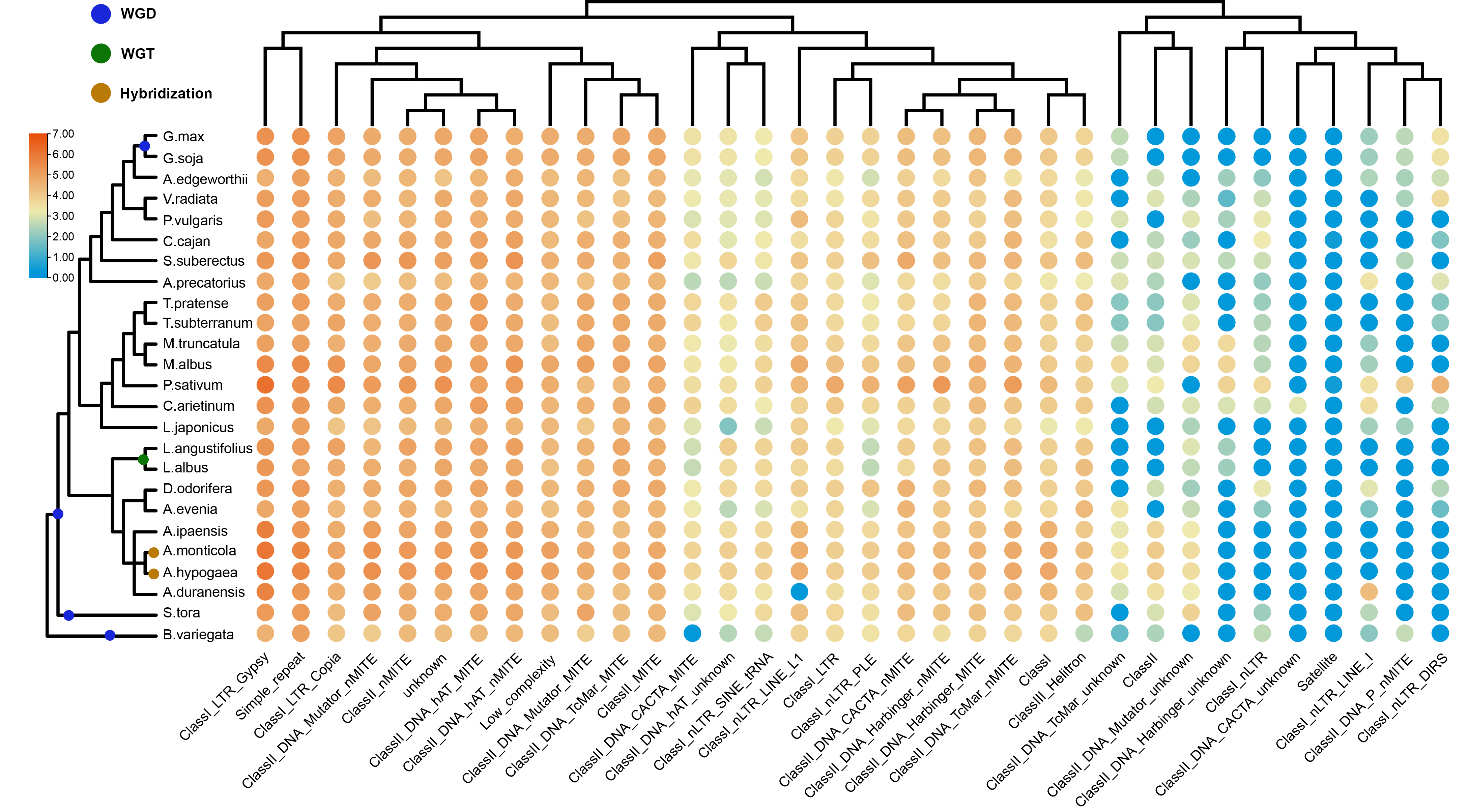
Transposable elements
Transposable elements (TEs): also known as jumping genes, are DNA sequences that can change their position in a cell. There are two types of transposons: type I transposons (Retrotransposon) and type II transposons (DNA transposons).
Type I transposons: DNA is used as a template and is transcribed into mRNA, which is then reverse transcribed into cDNA and inserted into a new position in the genome by the action of integrase. Type II transposon: The mechanism of transposition of type II transposon is called "cut-and-paste". The transposase cuts the TE from its original position in the genome and pastes it into other regions of the genome. The gaps formed by the cut are repaired by DNA.