Karyotype
-
Blast
Sequence alignment between arbitrary species -
ColinearScan
Syntenic matching tool -
Blastp dotplot
Plotting blastp dotplot diagrams -
Block dotplot
Drawing block dotplot function -
Correspondence_mc
Inter- and intra-genomic comparisons -
Fabaceae karyotype
Ancestral genome of Fabaceae -
Blast visualization
Matching visualization -
Syntenic visualization
Syntenic matching tool
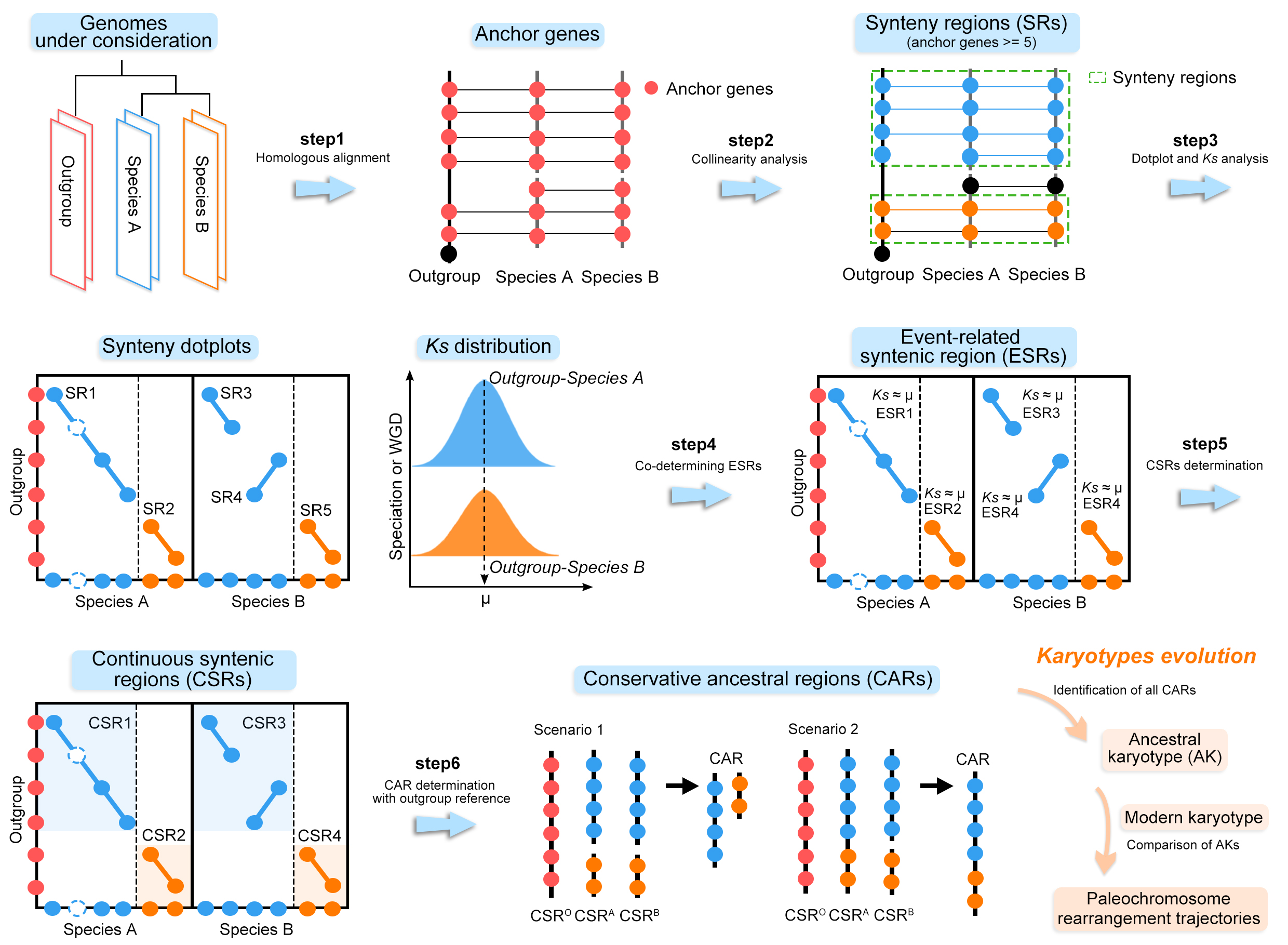
Inferring ancestral karyotypes and evolution
The inference of ancestral genome structure and paleogenome remodelling trajectories is divided into 7 main steps.
- Genome-wide comparison of the species involved, based on BLAST software, to confirm conserved homologous genes between and within genomes.
- The homology information obtained from BLASTP was entered into CollinearScan or MCScanX for collinearity analysis to identify the synteny blocks.
- Identification of orthologs and paralogs associated with speciation and polyploidy by inter- and intra-genomic comparisons.
- Identification of conserved ancestral regions (CARs) by the combination of dotplots and gene collinearity between genomes.
- Identification of ancient chromosomal rearrangements in conjunction with species trees.
- Then, by identifying and collating all the CAR rearrangements, we can bottom-up infer the ancestral karyotype and its composition of the study species.
- After determining the ancestral genome, we can identify the fusion patterns and rearrangement trajectories of paleochromosome by comparing the CRAs in the dotplot between the modern and ancestral genome.